How-To Optimize Your Website for On-Page SEO
How-To Optimize Your Website for On-Page SEO
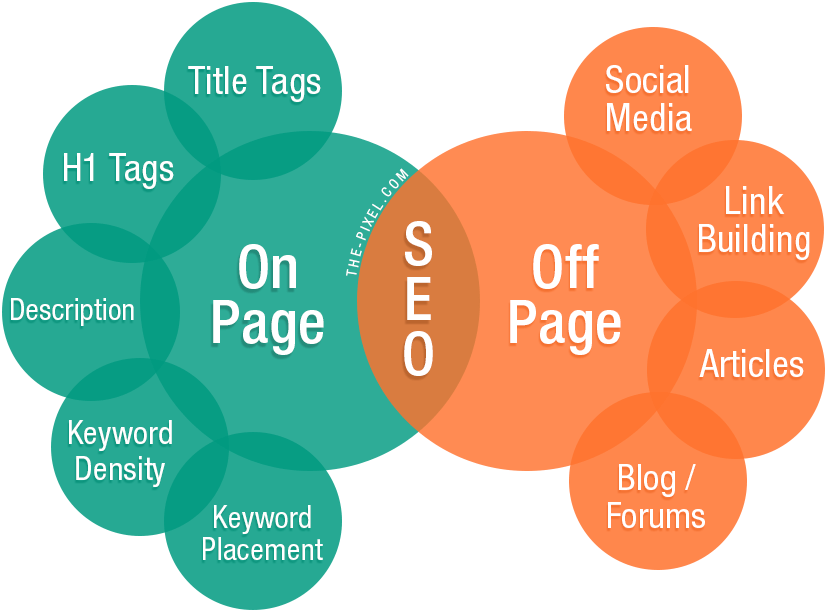
On-Page Optimization Best Practices
Best practices for creating a website that can endure algorithm updates. When you know what factors influence your on-page SEO, you can start optimizing them.
URL
What is a URL? Your URL is like an address, but for a page on the Internet.
URLs for your website’s pages should include brief descriptions of the page’s topic.
For example, if you have a page about doggie daycares in Delray Beach, a good URL for that would be www.yoursite.com/dog-daycares-in-delraybeach. Or, if you have multiple locations, you may use the following format: www.yoursite.com/locations/delraybeach/dog-daycare.
Including your keyword in your URL instead of a long string of jumbled numbers also makes your site easier to navigate and gives people a better idea of your page topics.
Which of the following URLs would you rather visit, for example?
- https://www.example.com/category/subcategory/keyword.html
- https://www.example.com/125typu4f5ww56fifl6639j875fe.html
Use clean, organized URLs — like the first example above — to improve your site’s architecture and help you rank higher in relevant search results.

Title Tag
What is a title tag? Your title tag is your page’s title, but it only appears in search results.
In order to show your website in search engine results pages (SERPs), Google has to know what your page is about.
Using specific keywords in the title tag of each page (<title>, </title>) makes it easier for search engine crawlers to understand your website.
For example, if you’re targeting the keyword, “dog daycare delray beach,” you may create the following title tag: “Top Dog Daycare in Delray Beach | Company Name.”
For the best results, limit your title tag to 55 characters to prevent Google from cutting it off in search results and use your targeted keyword at the beginning.
Meta Description
What is a meta description? Your meta description is your page’s summary and appears in SERPs.
A meta description doesn’t influence your on-page ranking optimization directly. It’s a feature that helps users, however, learn more about your page. The fact that Google will bold user search terms that appear in your meta description is another reason to optimize your meta description for on-page SEO.
Include your core and related keywords in your meta description for the best results. Your page about dog daycare in Delray Beach, for instance, may use the following meta description: “Looking for dog daycare in Delray Beach? Come to Fido’s for dog daycare, dog grooming, and more!”
For the best results, your meta description should stick to 160 characters.
An SEO plugins like Yoast or AIOSEO will automatically let you know if you’ve put too many characters in.

Heading Tags
What is a heading tag? Heading tags break up content with H2s, H3s, and H4s to improve its readability.
When it comes to heading tags, you want to use them for search engines and users.
Use heading tags throughout your content to break it up and make it easier to read when users are skimming for what they want.
You can also add your core or related keywords to provide search engines with more context for your page.
For example, a post about dog daycare may use the following headings:
- What does dog daycare include?
- How much does dog daycare cost?
- How to find the best dog daycare
When writing your heading tags, remember to target your core keyword in your H1 tag.
Alt Tags
What is an alt tag? Alt tags provide more information for multimedia, like images and videos.
Since search engines can’t read multimedia, they depend on alt attributes to tell them what multimedia is.
For example, if you have a photo of a puppy, your alt tag could say “mini long haired Dachshund puppy.” Beyond that, you can add descriptive names to the image files themselves so Google can get a better idea of your multimedia.
Always include an alt tag for your multimedia content. Besides Google, your alt tags also help users that can’t see or interact with your content. Using alt tags makes your content accessible to everyone browsing your site.
Keywords
What are keywords? Keywords describe words used in SEO to target valuable user queries.
Each page on your site should include text content that discusses the page’s topic.
Even pages that are typically not optimized, such as the “Contact Us” page, can help your business gain recognition online. Using keywords throughout the body text of your page helps Google read it and rank it appropriately.
You should research and compile keywords for each page on your site. Keyword research tools from Google can help you understand the keywords people research related to your products and services.
Look at helpful metrics, like monthly search volume and competition, to determine which keywords offer you the most value.
In most cases, smaller companies will focus on long-tail keywords or keywords with three to four words.
Long-tail keywords often have lower monthly search volumes, but they also have lower competition. It’s typically easier to decipher the search intent behind long-tail keywords since they are more specific.
For example, if someone searches the short-tail term, “dog treats,” it’s hard to identify exactly what they want to find. Maybe they’re researching the best organic dog treats for small dogs, or they might want to try a dog treat recipe.
On the other hand, if someone searches the long-tail phrase, “organic chew treats for puppies,” you know exactly what they want to find — and that they’re ready to purchase.
High-performing SEO campaigns contain both short and long-tail keywords — and the terms you choose to target will depend on your business and goals.

Content
What is content? Content provides users with answers and search engines with context.
Content is critical to on-page optimization.
With content, you give users a reason to visit your site.
Whether it’s to read a blog post or check out a product page, people browse your content. Optimizing your content can help search engines understand and rank your content, which can lead to people finding your website.
On-page SEO for content revolves around the following practices:
- Using your keywords in headings and paragraphs
- Breaking your content into simple headings
- Complementing your content with helpful images
- Ensuring your content uses correct spelling and grammar
- Making your content trustworthy and authoritative
In addition, you should regularly add new pages of content to your site so that search engines will see that you’re active online. You can do this with new blog posts, landing pages, and other strategies that show Google you’re hard at work for your customers.
Finding and removing duplicate content also improves your on-page SEO.
Duplicate content refers to blocks of similar content on multiple pages on your website — and its undesirable for two reasons:
- Google doesn’t know which page to rank: When numerous site pages contain the exact same information, search engines won’t know which page to rank in search results.
- Duplicate content confuses site visitors: When visitors encounter duplicate content on your site, it can confuse them, and they may not know what step to take next. Duplicate content throws a wrench in your content funnel and prevents your audience from taking action.
Duplicate content is bad for on-page SEO, so make sure to regularly check your site for duplicate content and remove it.
Again, a helpful SEO plugin can automatically do this for you.
Page Speed
What is page speed? Page speed measures how fast content on a page loads.
With an attention span of less than the common goldfish, 50% of users will abandon a page if it takes longer than three seconds to load. People want information, and they want it now!
Search engines like Google also use page speed as a ranking factor. You can control your site speed and page speed, so you want to optimize your page speed. Make your website load faster, and you can rank higher in search results.
Use Page Speed Insights to check your speed.
Page Speed Insights will provide you with customized recommendations for speeding up your site. You can also follow some best practices for page speed, like compressing images, eliminating unnecessary website code, and more.

Internal Linking
What is internal linking? Internal linking describes linking to and from pages on your website.
Internal linking often gets overlooked when it comes to on-page SEO. As your site grows, however, it’s critical to develop an internal linking process. That’s because internal linking helps crawlers explore your site, discover new content, and understand the context of different pages.
Having little to no internal linking on your pages negatively impacts the user’s ability to access content on your site that is valuable to them. And if they can’t access it, that directly affects your conversion rate.
Use internal links to improve your on-page SEO by:
- Adding links to relevant, existing content in new posts
- Adding links from relevant, existing content to new pages
Every internal linking strategy is different, but for the best results, you should make sure that every new page has at least two to three links to it. If you’re struggling to find pages, don’t force a link. Instead, consider creating pillar content.
You can check the status of your internal linking with a free tool like Semrush.
Images
What are images? Images are a form of multimedia that helps people understand and skim content.
Images matter to SEO, as well as users. With images, you can break up your content. You can also provide context, like for complicated processes or difficult-to-describe features. Include images in your content, from stock photos to custom graphics to screenshots.
When adding images to your site, remember to compress your images. Oversized multimedia can slow down your page speed, which can impact your rankings. Remember also to add alt text, as this additional detail makes your website more accessible and can help with rankings in Google Images.
Be sure to also include usability features such as transcriptions for videos and alternate text for images. These are another great place to include your target keywords, and incorporating them can help make your site ADA compliant.
Mobile-friendly
What is mobile-friendliness? Mobile-friendliness describes your site’s usability on mobile devices.
A mobile-friendly website is essential because more than 50% of the Internet’s traffic comes from mobile devices. If people on smartphones and tablets can’t access your site, your rankings in search results will go down.
Search engines like Google, for example, use mobile-friendliness or responsiveness as a ranking factor. This means, if your site isn’t optimized for mobile users, you’re missing out on valuable leads and revenue.
Mobile compatibility isn’t a suggestion anymore. It’s a requirement, especially if you want to rank well for your keywords. Google considers mobile compatibility when it ranks your website. Low compatibility = low rank.
On-page optimization for mobile-friendliness often focuses on developing a responsive site. With a responsive website, you have a single site, which makes it easy to update your website and add new content.
Mobile is close to our heart—we love seeing more and more sites make their content available in useful and accessible ways for mobile users. Let’s discuss your mobile-friendly website!
Hire ThePixel to build your next website!
Since our founding in 2008, we’ve created and launched many types of business websites. Over the last decade and we’ve learned a thing or two! That’s why we’re masters of our craft, let us help you build the website of your dreams – one that generates traffic, leads and conversions.
Are you ready to start? If yes, contact ThePixel and one of our representatives will guide you through the website phases and how the process works either by a Zoom Meeting or phone.